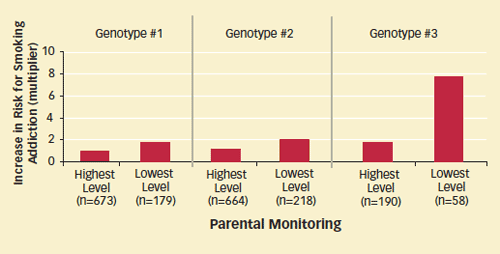
 Gene Variant and Low Parental Monitoring Combine to Elevate Smoking Risk: Increased risk of nicotine addiction conferred by one genotype of CHRNA5 dramatically increases among people who experienced low parental supervision as young teens.
Gene Variant and Low Parental Monitoring Combine to Elevate Smoking Risk: Increased risk of nicotine addiction conferred by one genotype of CHRNA5 dramatically increases among people who experienced low parental supervision as young teens.This bar graph, titled "Gene Variant and Low Parental Monitoring Combine to Elevate Smoking Risk," displays increased risk of nicotine addiction on the vertical axis and the level of parental monitoring on the horizontal axis. Data for three genotypes of CHRNA5 are presented.
In Genotype 1, the highest level of parental monitoring (n=673) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 1, while the lowest level of parental monitoring (n=179) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 2.
In Genotype 2, the highest level of parental monitoring (n=664) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 1, while the lowest level of parental monitoring (n=218) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 2.
In Genotype 3, the highest level of parental monitoring (n=190) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 2, while the lowest level of parental monitoring (n=58) had a multiplier of an increase in risk for smoking addition of 8.
