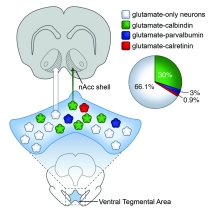
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) in the brain participates in the rewarding effects of drug use, but the role of specific neurons within the VTA is unclear. Scientists at NIDA’s Intramural Research Program (IRP) conducted a set of studies to better understand the function of glutamate neurons in this addiction-relevant brain region. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter that plays an important role in brain development, normal brain processes, and pathological conditions like addiction.
Studying the rat brain, the investigators discovered that the calcium-binding protein calbindin is expressed in approximately 30% of all VTA glutamate neurons. They also found that approximately 20% of these VTA neurons express molecules for the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the reinforcing effects of addictive drugs. The researchers then went on to show that 80% of the glutamate neurons expressing calbindin that project to the nucleus accumbens shell — another area of the brain involved in the rewarding effects of drugs — also express dopamine. These findings broaden our understanding of the diversity of VTA neurons and identify a subpopulation of calbindin neurons with the capability to co-release glutamate and dopamine in the nucleus accumbens shell. Further studies are necessary to determine the role these neurons play in behavior.
Study:
- Smriti Mongia, Tsuyoshi Yamaguchi, Bing Liu, Shiliang Zhang, Huiling Wang, and Marisela Morales. The Ventral Tegmental Area has calbindin neurons with the capability to co-release glutamate and dopamine into the nucleus accumbens. European Journal of Neuroscience.