Organizational Chart
- Text Description of Organizational Chart
Office of the Director
Nora D. Volkow, M.D.
Director
Wilson Compton, M.D., M.P.E.
Deputy Director
Joellen Austin, MPAff, MSM
Deputy Director for ManagementDivision of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences
Kurt Rasmussen, Ph.D.
DirectorDivision of Neuroscience and Behavior
Rita Valentino, Ph.D.
DirectorCenter for the Clinical Trials Network
Betty Tai, Ph.D.
DirectorDivision of Epidemiology, Services and Prevention Research
Carlos Blanco, M.D., Ph.D.
DirectorIntramural Research Program
Amy Newman, Ph.D.
Acting Scientific DirectorOffice of Science Policy and Communications
Jack B. Stein, Ph.D.
DirectorDivision of Extramural Research
Susan Weiss, Ph.D.
DirectorOffice of Management
Joellen Austin, MPAff, MSM
Director
Appropriation Language
For carrying out section 301 and title IV of the PHS Act with respect to drug abuse, [$1,462,016,000] $1,431,770,000.
Tables
- Budget Mechanism
Budget Mechanism - Total1 (Dollars in Thousands) Mechanism FY 2019
FinalFY 2020
EnactedFY 2021
President's
BudgetFY 2021
+/-
FY 2020
EnactedNo. Amount No. Amount No. Amount No. Amount Ruth L. Kirschstein Training Awards FTTPs FTTPs FTTPs FTTPs Research Projects: Noncompeting 975 $550,168 991 $687,542 994 $722,367 3 $34,825 Administrative Supplements (151) 14,149 (95) 9,280 (84) 8,200 (-11) -1,080 Competing: Renewal 29 16,817 55 32,000 30 17,000 -25 -15,000 New 371 275,997 344 222,459 329 187,014 -15 -35,445 Supplements 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Subtotal, Competing 400 $292,813 399 $254,459 359 $204,014 -40 -$50,445 Subtotal, RPGs 1,375 $857,131 1,390 $951,280 1,353 $934,581 -37 -$16,700 SBIR/STTR 108 48,686 89 41,534 87 40,725 -2 -808 Research Project Grants 1,483 $905,817 1,479 $992,814 1,440 $975,306 -39 -$17,508 Research Centers: Specialized / Comprehensive 28 $64,305 30 $55,495 32 $54,407 2 -$1,088 Clinical Research 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Biotechnology 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Comparative Medicine 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Research Centers in Minority Institutions 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Research Centers 28 $64,305 30 $55,495 26 $54,407 2 -$1,088 Other Research: Research Careers 220 $40,453 230 $42,252 221 $41,326 -9 -$926 Cancer Education 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Cooperative Clinical Research 19 90,935 27 50,135 27 48,974 0 -1,161 Biomedical Research Support 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Minority Biomedical Research Support 0 1,282 0 1,311 0 1,282 0 -29 Other 57 15,010 59 17,628 57 17,366 -2 -262 Other Research 296 $147,680 316 $111,326 305 $108,948 -11 -$2,378 Total Research Grants 1,807 $1,117,802 1,825 $1159,635 1,777 $1,138,661 -48 -$20,974 Individual Awards 104 $4,678 106 $4,865 104 $4,758 -2 -$107 Institutional Awards 370 21,030 379 21,871 370 21,389 -9 -482 Total Research Training 474 $25,708 485 $26,736 474 $26,147 -11 -$589 Research and Development Contracts 93 $98,965 93 $95,574 93 $94,997 0 -$577 (SBIR/STTR) (non-add) (12) (4,067) (15) (5,177) (15) (5,177) (0) (0) Intramural Research 117 96,233 117 100,248 117 98,043 0 -2,205 Res. Management & Support 240 69,507 265 75,531 265 73,922 0 -1,609 Res. Management & Support (SBIR Admin) (non-add) (0) (258) (0) (360) (0) (360) (0) (300) Construction 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Buildings and Facilities 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total, NIDA 357 $1,408,216 382 $1,457,724 382 $1,431,770 0 -$25,954 1 All numbers in italics and brackets are non-add entries.
- Amounts Available for Obligation
(Dollars in Thousands)1 Source of Funding FY 2019
FinalFY 2020
EnactedFY 2021
President's
BudgetAppropriation $1,419,844 $1,462,016 $1,431,770 Mandatory Appropriation: (non-add)
Type 1 Diabetes(0) (0) (0) Mandatory Appropriation: (non-add)
Other Mandatory financing(0) (0) (0) Rescission 0 0 0 Sequestration 0 0 0 Secretary's Transfer -3,249 0 0 Subtotal, adjusted appropriation $1,416,595 $1,462,016 $1,431,770 OAR HIV/AIDS Transfers -8,379 -4,292 0 HEAL Transfer from NINDS 0 0 0 Subtotal, adjusted budget authority $1,408,216 $1,457,724 $1,431,770 Unobligated balance, start of year2 213,124 0 0 Unobligated balance, end of year 0 0 0 Subtotal, adjusted budget authority $1,621,340 $1,457,724 $1,431,770 Unobligated balance lapsing -6 0 0 Total obligations $1,621,334 $1,457,724 $1,431,770 1Excludes the following amounts for reimbursable activities carried out by this account:
FY 2019 - $16,549 FY 2020 - $12,931 FY 2021 - $12,850
2 Reflects HEAL Initiative funding not obligated in FY 2018, and carried over into FY 2019.- Summary of Changes
(Dollars in Thousands) FY 2020 Enacted $1,457,724 FY 2021 President's Budget $1,431,770 Net change -$25,954 CHANGES 2021 President's Budget:
FTEs2021President's Budget:
Budget AuthorityChange from FY 2020:
FTEsChange from FY 2020:
Budget AuthorityA. Built-in: 1. Intramural Research: a. Annualization of January 2020 pay increase & benefits $27,984 $366 b. January FY 2021 pay increase & benefits 27,984 512 c. Paid days adjustment 27,984 -209 d. Differences attributable to change in FTE 27,984 0 e. Payment for centrally furnished services 11,812 -1,243 f. Cost of laboratory supplies,
materials, other expenses, and
non-recurring costs58,246 -85 Subtotal -$660 2. Research Management and Support: a. Annualization of January 2020 pay
increase & benefits$42,377 $271 b. January FY 2021 pay increase & benefits 42,377 417 c. Paid days adjustment 42,377 -158 d. Differences attributable to change in FTE 42,377 0 e. Payment for centrally furnished services 2,751 -814 f. Cost of laboratory supplies,
materials, other expenses, and
non-recurring costs28,794 226 Subtotal -$58 Subtotal, Built-in -$718 Summary of Changes - Continued
(Dollars in Thousands)CHANGES Fy 2021 President's Budget:
No.Fy 2021 President's Budget:
AmountChange from
FY 2020 Enacted:
No.Change from
FY 2020 Enacted:
AmountB. Program: 1. Research Project Grants: a. Noncompeting 994 $730,567 3 $33,745 b. Competing 359 204,014 -40 -50,445 c. SBIR/STTR 87 40,725 -2 -808 Subtotal, RPGs 1,440 $975,306 -39 -$17,508 2. Research Centers 32 $54,407 2 -$1,088 3. Other Research 305 108,948 -11 -2,378 4. Research Training 474 26,147 -11 -589 5. Research and development contracts 93 94,997 0 577 Subtotal, Extramural $1,259,805 -$22,140 FTEs FTEs 6. Intramural Research 117 $98,043 0 -$1,545 7. Research Management and Support 265 73,922 0 -1,551 8. Construction 0 0 9. Buildings and Facilities 0 0 Subtotal, program 382 $1,431,770 0 -$25,236 Total changes -$25,954 - Authorizing Legislation
PHS Act/Other Citation U.S. Code Citation 2020 Amount Author-
izedFY 2020 Enacted 2021 Amount Author
-izedFY 2021 President's Budget Research and Investigation Section 301 42§241 Indefinite $1,457,724,000 Indefinite $1,431,770,000 National Institute on Drug Abuse Section 401(a) 42§281 Indefinite Indefinite Total, Budget Authority $1,457,724,000 $1,431,770,000 - Appropriations History
Fiscal Year Budget Estimate to Congress House Allowance Senate Allowance Appropriation 2012 $1,080,018,000 $1,080,018,000 $1,038,714,000 $1,055,362,000 Rescission $1,994,634 2013 $1,054,001,000 $1,057,196,000 $1,053,367,366 Rescission $2,106,735 Sequestration ($52,871,798) 2014 $1,071,612,000 $1,064,490,000 $1,025,435,000 Rescission $0 2015 $1,023,268,000 $1,028,614,000 Rescission $0 2016 $1,047,397,000 $1,050,875,000 $1,069,086,000 $1,077,488,000 Rescission $0 20171 $1,050,550,000 $1,107,700,000 $1,103,032,000 1,090,853,000 Rescission $0 2018 $864,998,000 $1,107,497,000 $1,113,442,000 $1,383,603,000 Rescission $0 2019 $1,137,403,000 $1,400,126,000 $1,420,591,000 $1,419,844,000 Rescission $0 2020 $1,296,379,000 $1,489,237,000 $1,490,498,000 $1,462,016,000 Rescission $0 2021 $1,431,770,000 1Budget Estimate to Congress includes mandatory financing.
- Budget Authority by Activity
(Dollars in thousands)1 Extramural Research FY 2019
FinalFY 2020
EnactedFY 2021
President's
BudgetFY 2021
+/-
FY 2020FTE Amount FTE Amount FTE Amount FTE Amount Detail: Division of Neuroscience and Behavior $452,177 $466,580 $456,433 $-10,147 Division of Epidemiology, Services and Prevention Research 323,147 333,440 326,188 -7,252 Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences 133,544 137,798 134,801 -2,997 Center for the Clinical Trials Network 39,743 41,009 40,117 -892 Office of Translational Initiatives and Program Innovations 37,988 39,197 38,345 -852 Opioid Crisis2 257,843 266,321 266,321 0 Subtotal, Extramural $1,244,442 $1,284,345 $1,262,205 -$22,140 Intramural Research 117 $96,233 117 $100,248 117 $98,043 0 -$2,205 Research Management & Support3 240 $67,540 265 $73,131 265 $71,522 0 -$1,609 TOTAL 357 $1,408,216 382 $1,457,724 382 $1,431,770 0 -$25,954 1Includes FTEs whose payroll obligations are supported by the NIH Common Fund.
2Opioid Crisis amount includes Research Management and Support as follows (in thousands): $1,967 in FY 2019, $2,400 in FY 2020, and $2,400 in FY 2021.
3Research Management and Support excludes funding related to opioid research.- Budget Authority by Object Class
(Dollars in Thousands)1 FY 2020 Enacted FY 2021 President's Budget FY 2021 +/- FY 2020 OBJECT CLASSES FY 2020 Enacted FY 2021 President's Budget FY 2021 +/- FY 2020 Total compensable workyears: Full-time employment 382 382 0 Full-time equivalent of overtime and holiday hours 0 0 0 Average ES salary $0 $0 $0 Average GM/GS grade 27.5 27.8 0.3 Average GM/GS salary $124 $126 $2 Average salary, grade established by act of July 1, 1944 (42 U.S.C. 207) $115 $115 $0 Average salary of ungraded positions $132 $132 $0 Personnel Compensation: 11.1 Full-time permanent 31,719 32,083 365 11.3 Other than full-time permanent 13,049 13,199 150 11.5 Other personnel compensation 1,472 1,489 17 11.7 Military personnel 754 774 20 11.8 Special personnel services payments 5,491 5,554 63 11.9 Subtotal Personnel Compensation $52,485 $53,100 $615 12.1 Civilian personnel benefits 16,034 16,660 625 12.2 Military personnel benefits 586 602 16 13.0 Benefits to former personnel 0 0 0 Subtotal Pay Costs $69,106 $70,362 $1,256 21.0 Travel and transportation of persons 1,359 1,286 -73 22.0 Transportation of things 75 76 1 23.1 Rental payments to GSA 0 0 0 23.2 Rental payments to others 0 0 0 23.3 Communications, utilities and misc. charges 288 294 6 24.0 Printing and reproduction 0 0 0 25.1 Consulting services 3,524 2,595 -930 25.2 Other services 12,861 12,773 -88 25.3 Purchase of goods and services from government accounts 124,294 125,269 975 25.4 Operation and maintenance of facilities 641 644 3 25.5 Research and development contracts 58,317 54,217 -4,100 25.6 Medical care 357 371 14 25.7 Operation and maintenance of equipment 5,995 6,115 120 25.8 Subsistence and support of persons 0 0 0 25.0 Subtotal Other Contractual Services $205,989 $201,984 -$4,100 26.0 Supplies and materials 4,692 4,786 94 31.0 Equipment 2,850 2.907 57 32.0 Land and structures 0 0 0 33.0 Investments and loans 0 0 0 41.0 Grants, subsidies and contributions 1,173,363 1,150,073 -23,290 42.0 Insurance claims and indemnities 0 0 0 43.0 Interest and dividends 2 2 0 44.0 Refunds 0 0 0 Subtotal Non-Pay Costs $1,388,618 $1,361,408 -$27,210 Total Budget Authority by Object Class $1,457,724 $1,431,770 -$25,954 1Includes FTEs whose payroll obligations are supported by the NIH Common Fund.
- Salaries and Expenses
(Dollars in Thousands) OBJECT CLASSES FY 2020 Enacted FY 2021 President's Budget FY 2021 +/- FY 2020 Personnel Compensation: Full-time permanent (11.1) $31,719 $32,083 $365 Other than full-time permanent (11.3) 13,049 13,199 150 Other personnel compensation (11.5) 1,472 1,489 17 Military personnel (11.7) 754 774 20 Special personnel services payments (11.8) 5,491 5,554 63 Subtotal Personnel Compensation (11.9) $52,485 $53,100 $615 Civilian personnel benefits (12.1) $16,034 $16,660 $625 Military personnel benefits (12.2) 586 602 16 Benefits to former personnel (13.0) 0 0 0 Subtotal Pay Costs $69,106 $70,362 $1,256 Travel and transportation of persons (21.0) $1,359 $1,286 -$73 Transportation of things (22.0) 75 76 1 Rental payments to others (23.2) 0 0 0 Communications, utilities and miscellaneous charges (23.3) 288 294 6 Printing and reproduction (24.0) 0 0 0 Other Contractual Services: Consultant services (25.1) 3,524 2,595 -930 Other services (25.2) 12,861 12,773 -88 Purchases from government accounts (25.3) 84,325 80,113 -4,212 Operation and maintenance of facilities (25.4) 641 644 3 Operation and maintenance of equipment (25.7) 5,995 6,115 120 Subsistence and support of persons (25.8) 0 0 0 Subtotal Other Contractual Services $107,345 $102,240 -$5,106 Supplies and materials (26.0) $4,692 $4,786 $94 Subtotal Non-Pay Costs $113,760 $108,682 -$5,078 Total Administrative Costs $182,866 $179,044 -$3,822 - Details of Full-Time Equivalent Employment (FTEs)
OFFICE/
DIVISIONFY 2019
FinalFY 2020
EnactedFY 2021
President's BudgetCivilian Military Total Civilian Military Total Civilian Military Total Division of Neuroscience and Behavior Direct: 25 0 25 25 0 25 25 0 25 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 25 0 25 25 0 25 25 0 25 Division of Epidemiology, Services and Prevention Research Direct: 20 2 22 26 2 28 26 2 28 Reimbursable: 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 Total: 21 2 23 27 2 29 27 2 29 Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences Direct: 26 0 26 30 0 30 30 0 30 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 26 0 26 30 0 30 30 0 30 Center for the Clinical Trials Network Direct: 10 0 10 13 0 13 13 0 13 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 10 0 10 13 0 13 13 0 13 Division of Extramural Research Direct: 54 0 54 55 0 55 55 0 55 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 54 0 54 55 0 55 55 0 55 Office of the Director Direct: 14 0 14 17 0 17 17 0 17 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 14 0 14 17 0 17 17 0 17 Office of Management Direct: 32 0 32 37 0 37 37 0 37` Reimbursable: 37 0 37 37 0 37 37 0 37 Total: 69 0 69 74 0 74 74 0 74 Office of Science Policy and Communication Direct: 22 0 22 23 0 23 23 0 23 Reimbursable: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Total: 22 0 22 23 0 23 23 0 23 Intramural Research Program Direct: 109 4 113 109 4 113 109 4 113 Reimbursable: 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 Total: 110 4 114 110 4 114 110 4 114 Total (Includes FTEs whose payroll obligations are supported by the NIH Common Fund) 351 6 357 376 6 382 376 6 382 FTEs supported by funds from Cooperative Research and Development Agreements 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fiscal Year Average GS Grade 2017 12.7 2018 13.0 2019 13,3 2020 13.2 2021 13.2 - Detail of Positions
Detail of Positions1 GRADE FY 2019 Final FY 2020 Enacted FY 2021 President's Budget Total, ES Positions 1 1 1 Total, ES Salary 192,254 192,254 192,254 GM/GS-15 62 62 62 GM/GS-14 66 66 66 GM/GS-13 63 63 63 GS-12 43 43 43 GS-11 15 15 15 GS-10 0 0 0 GS-9 5 5 5 GS-8 7 7 7 GS-7 8 8 8 GS-6 2 2 2 GS-5 0 0 0 GS-4 0 0 0 GS-3 0 0 0 GS-2 0 0 0 GS-1 0 0 0 Subtotal 271 271 271 Grades established by Act of July 1, 1944 (42 U.S.C. 207): 0 0 0 Assistant Surgeon General 0 0 0 Director Grade 0 0 0 Senior Grade 4 4 4 Full Grade 1 1 1 Senior Assistant Grade 1 1 1 Assistant Grade 0 0 0 Subtotal 6 6 6 Ungraded 90 90 90 Total permanent positions 277 277 277 Total positions, end of year 368 382 382 Total full-time equivalent (FTE) employment, end of year 357 382 382 Average ES salary 192,254 192,254 192,254 Average GM/GS grade 13.3 13.2 13.2 Average GM/GS salary 123,465 124,408 125,652 1Includes FTEs whose payroll obligations are supported by the NIH Common Fund.
Budget Graphs
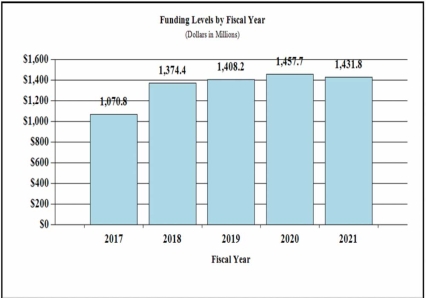
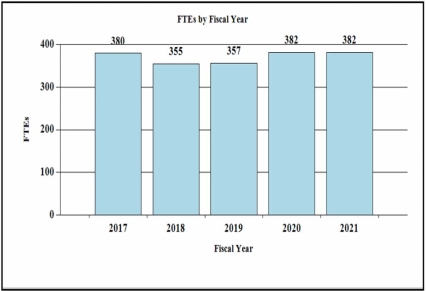
History of Budget Authority and FTEs:
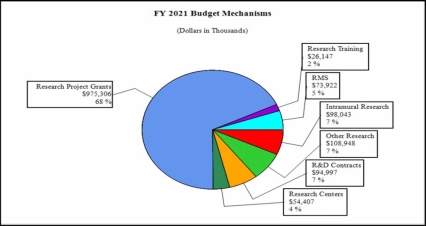
Distribution by Mechanism (dollars in thousands):
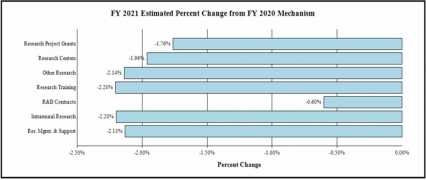
Change by Selected Mechanism:
Justification of Budget Request
National Institute on Drug Abuse
Authorizing Legislation: Section 301 and Title IV of the Public Health Service Act, as amended.
| FY 2019 Final | FY 2020 Enacted | FY 2021 President's Budget | FY 2021 +/- FY 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | $1,408,216,000 | $1,457,724,000 | $1,431,770,000 | -25,954,000 |
| FTE | 357 | 382 | 382 | 0 |
Program funds are allocated as follows: Competitive Grants/Cooperative Agreements; Contracts; Direct Federal/Intramural and Other.
Major Changes in the Fiscal Year 2021 President’s Budget Request
Major changes by budget mechanism and/or budget activity detail are briefly described below. Note that there may be overlap between budget mechanism and activity detail and these highlights will not sum to the total change for the FY 2021 President’s Budget. The FY 2021 President’s Budget for NIDA is $1,431.8 million, a decrease of $26.0 million from FY 2020.
- Research Project Grants (RPGs) (-$17.5 million; total $975.3 million):
NIDA will reduce funding for non-competing RPGs by 7.0 percent which is a $38.5 million decrease from their full funding level. The number of competing RPGs is expected to decrease by 40 grants compared to the FY 2020 level of 399 awards. The amount of support to competing awards will be reduced by $50.4 million from FY 2020, a 19.8 percent reduction. These reductions are distributed across programmatic areas and basic, epidemiology or clinical research.
- Research Centers (-$1.1 million; total $54.4 million): NIDA will reduce non-competing awards by 2.0 percent and fund fewer new and competing awards.
- Other Research (-$2.4 million; total $108.9 million): NIDA will reduce non-competing awards by 2.0 percent and fund fewer new and competing awards.
- Ruth L Kirchstein Training (-$589,000; total $26.1 million): NIDA will fund fewer new and competing awards.
Director’s Overview
Substance misuse and addiction have grown dramatically over the last several decades as major public health challenges that exact an enormous toll on society. Nearly 19 million people in the United States suffer from a substance use disorder (SUD), and drug overdoses claimed the lives of more than 70,000 people in 2017.1 The mission of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is to advance science on the causes and consequences of drug use and addiction and apply that knowledge to improve individual and public health. In the last 20 years, research supported by NIDA has transformed our understanding of addiction and how to address it. With the continued support of Congress, including for the trans-agency NIH Helping to End Addiction Long-termSM (HEAL) Initiative, NIDA is poised to accelerate progress toward scientific solutions to addiction and the devastating consequences it has for public health.
Once viewed as a conscious choice or character flaw, addiction is now understood as a chronic brain disorder that can be treated, and from which one can recover. This view is supported by decades of research demonstrating the complex social and biological factors that contribute to substance misuse and addiction, including the profound and long-lasting effects that addictive drugs have on the brain. Aided by efforts like the NIH Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative, which is driving the development of new tools for studying and manipulating neural function, NIDA continues to advance fundamental research in this area.
Two NIDA-led studies are pushing the boundaries of understanding how drugs and other childhood exposures affect the developing human brain: the Adolescent Brain and Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study and the HEALthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) study. In FY2019, the ABCD study completed the recruitment of over 11,000 children ages 9-10 and will follow them into adulthood. The study integrates brain imaging with genetic, psychological, behavioral, and other health data, to elucidate factors that enhance or disrupt a young person’s life trajectory. The HBCD study, started in FY2019 and still in its pilot phase, aims to follow a large sample of children from the prenatal period through early childhood, enabling researchers to collect information on normal brain development, the influence of genes and diverse social environments on this development and the long-term impact of pre and postnatal drug use.
NIDA is also supporting research using neuroimaging, genomics, and behavioral assessments to identify biomarkers of addiction-related behavior, diagnosis, and prognosis. For example, a recent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study of smokers found that activity in a particular brain region pinpointing specific biomarkers may uncover modifiable risk and resilience factors, paving the way for novel, tailored, and effective prevention and treatment interventions.
The landscape of drug use in our country has changed over the last two decades, as dominance has shifted from prescription opioids, to heroin, to potent synthetic opioids and most recently psychostimulant drugs (cocaine and methamphetamine).2 Drug overdoses are now the nation’s leading cause of unintentional fatal injury.3 At the same time, changes in marijuana policy at the state level have increased its availability and the number of people consuming it, and the marijuana being used is much more potent than it was two decades ago. The emergence and rapid uptake of e-cigarettes and vaping have changed the way that nicotine and cannabis are being consumed, resulting in new health risks. Epidemiological studies supported by NIDA are critical to tracking patterns of drug use such as the Monitoring the Future study, which surveys teenage drug use, and the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health study, which assess patterns of tobacco and nicotine use. Such studies not only provide timely information on drug trends, but they inform the development of interventions for preventing and treating substance misuse.
Indeed, the last 20 years have witnessed important advances in prevention and treatment. For example, a large body of research shows that preventive interventions aimed at strengthening the family and community relationships of children can reduce subsequent drug use. NIDA is leveraging its growing understanding of the complex determinants and consequences of SUD to develop more personalized preventive interventions. Big Data analysis and statistical modeling techniques, which can be used to predict vulnerabilities and delineate meaningful comorbidity patterns, are being leveraged toward this goal, such as ongoing research to model the specific resource needs of communities hard hit by the opioid crisis. NIDA is also supporting research to identify new risk and protective factors for addiction and its consequences, and to deploy prevention interventions at key points of vulnerability, such as during the transition from adolescence into young adulthood.
Our growing understanding of how the nervous system is affected by drugs has led to new addiction treatments, such as buprenorphine for opioid addiction, lofexidine to mitigate opioid withdrawal, and nasal Narcan to reverse opioid overdose. Medication development continues to be a priority for NIDA under the HEAL Initiative (see below), with efforts underway to develop new drugs for treating addiction, reversing overdose, and mitigating the symptoms of withdrawal. NIDA has also used technology to explore and implement evidence-based interventions via telemedicine and mobile health care, including supporting the development of ReSET and ReSET-O, the first FDA-approved mobile applications for behavioral treatment of SUD and opioid use disorder (OUD). Additionally, NIDA supports research testing the potential of devices that alter neural activity for addiction treatment, such as trans-cranial magnetic stimulation for SUD.
Although great strides have been made toward the acceptance of addiction as a brain disorder within the scientific and clinical communities, more work is needed to ensure that evidence-based interventions that reflect the chronic nature of addiction are integrated into medical practice and public health strategy. To maximize the impact of research advances in addiction medicine, NIDA supports implementation science research for SUD treatment and prevention in a variety of settings, including health care (e.g., primary care offices, hospitals, and emergency rooms) and justice (e.g., prisons) settings. NIDA also supports research to assess the impact of Federal-, state-, and systems-level policies related to drug use and SUD on public health and well-being, as well as to increase strategic partnerships within communities to improve the translation of research into policy and practice. Two large NIDA studies are currently researching the effective implementation of evidence-based strategies for struggling communities (the HEALing Communities Study) and vulnerable populations (the Justice Communities Opioid Innovation Network), as described below.
Over the last several decades, researchers have propelled our understanding of addiction forward. This progress was made possible, in part, through the development of cutting-edge tools and techniques that have given researchers unprecedented ability to interrogate the causes and consequences of substance use disorders and develop interventions to prevent and treat them. NIDA is poised to build on these advances in addiction science to bring new solutions to bear on one of the nation’s most pressing public health crises.
Overall Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request for NIDA is $1,431.8 million, a decrease of $26.0 million or 1.8 percent below the FY 2020 Enacted level. Within this funding level, amounts budgeted for the HEAL Initiative will be equal to the FY 2020 level. Other funding for opioid and pain research in the FY 2021 request will likewise be no less than the FY 2020 level. FY 2021 funding includes an additional $50.0 million for research to develop medication-assisted treatment and evidence-based psychosocial treatment to support the strategy to reduce the use of methamphetamines.
Program Description and Accomplishments
Responding to the Opioid Crisis
As part of the resources to support the HEAL initiative, NIDA will continue to expand its support for new research efforts to combat opioid addiction. Projects are currently underway to develop novel prevention and treatment strategies for OUD and to translate evidence-based interventions into effective medical practice. For example, NIDA is supporting a study to prevent the high rate of opioid misuse initiation associated with the transition from adolescence to adulthood. To accelerate availability of novel treatments, a focused medication development program is supporting a series of targeted studies with the goal of submitting approximately 15 investigational new drug and 5 new drug applications to the FDA for medications to prevent and treat OUD and overdose.
NIDA HEAL funds have also been targeted toward expansion of the National Drug Abuse Treatment Clinical Trials Network (CTN) through additions of new nodes and protocols. Two large projects within the CTN are addressing knowledge gaps around treatment initiation and retention. The first is a study of the efficacy of prevention interventions to arrest the progression from risky opioid use to more severe OUD. Researchers will test the efficacy of a Subthreshold Opioid Use Disorder Prevention (STOP) intervention in primary care settings that will identify and address early-stage opioid misuse. The second is a study to test strategies to improve retention in medication-based treatment for OUD, as well as strategies to improve outcomes among patients who have been stabilized on OUD medications and want to stop taking them. This will be the first study of medications to treat OUD to prospectively follow a large sample of patients through discontinuation.
Concentrated efforts under HEAL are also determining effective implementation strategies for evidence-based interventions. The Justice Community Opioid Innovation Network (JCOIN) will study approaches to increase high-quality care for people with opioid misuse and OUD in justice populations. JCOIN will test strategies to expand effective treatment and care in partnership with local and state justice systems and community-based treatment providers. The HEALing Communities Study, a multi-site implementation research study, will investigate coordinated approaches for deploying evidence-based strategies for preventing and treating opioid misuse and OUD to determine which are most effective at the local level.
Finally, the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study adds to NIDA’s robust portfolio of research seeking to understand brain development trajectories and how they may be shaped by drug exposure. This study will create a cohort of pregnant women and follow their children through the first decade of their life to determine how environmental factors, including maternal drug exposure and genetics, influence early brain development along with behavioral and clinical outcomes (including mental illnesses and addiction).
Program Portrait: Determining strategies to reduce opioid overdose in communities hardest hit by the opioid crisis (the HEALing Communities Study)
Effective prevention and treatment programs and services exist to address opioid misuse, opioid use disorder (OUD), and overdose. However, many people who need these programs and services do not receive them, in part because of a need to better understand how to make them most effective at a local level. For communities to successfully address their opioid crises, they need implementation strategies that take their unique local needs and resources into account.
NIH and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) launched the HEALing Communities Study to investigate how tools for preventing and treating opioid misuse and OUD are most effective at the local level. This multi-site implementation research study will test the impact of an integrated set of evidence-based practices across health care, behavioral health, justice, and other community-based settings. The goal of the study is to reduce opioid-related overdose deaths by 40 percent over the course of three years. Research sites are partnering with 67 communities highly affected by the opioid crisis in 4 states to measure the impact of these efforts. The study will also look at the effectiveness of coordinated systems of care designed to increase the number of individuals receiving medication to treat OUD, increase the distribution of naloxone, and reduce high-risk opioid prescribing.
Through the NIH HEAL Initiative, NIH awarded four grants to academic institutions in Kentucky, Massachusetts, New York, and Ohio to conduct research as part of the HEALing Communities Study. The awards will support research on the effectiveness of a comprehensive, data-driven, community-engaged intervention designed to increase the adoption of an integrated set of evidence-based practices to reduce opioid-related overdose deaths and associated outcomes. Additionally, a grant was awarded to RTI International to serve as the study’s coordinating center. RTI will be responsible for data analysis, health economics research, and widespread dissemination of research findings over the course of the study.
The research institutions and their community partners will work with local coalitions to develop and deploy comprehensive, data-driven plans to implement evidence-based practices across multiple community sectors to reduce opioid overdose deaths and address associated outcomes. The intervention seeks to promote a common vision, shared goals, and tailored strategies to mobilize communities to adopt evidence-based practices. The intervention will use a stepwise community change process with three components: community engagement, system- and practice-level changes to increase adoption of evidence-based practices across the continuum of care, and a community-based communication campaign.
Program Portrait: Studying the effects of environmental factors, including opioids and other substance use, on early brain development from pregnancy through early childhood (HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study)
The first few years of life are a period of exponential brain growth and development. It is not currently known how infant and childhood development is affected by early exposure to opioids. To address this knowledge gap, NIH is supporting research to better understand typical brain development, beginning in the prenatal period and extending through early childhood, including variability in development and how it contributes to cognitive, behavioral, social, and emotional function.
The HEALthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) Study will establish a large cohort of pregnant women from regions of the country significantly affected by the opioid crisis and follow them and their children for at least 10 years. Research from this cohort will help understand normative childhood brain development as well as the long-term impact of pre- and postnatal opioid and other drug and adverse environmental exposures. The study will collect data on pregnancy and fetal measures; infant and early childhood structural and functional brain imaging; measurements of body shape and size; medical history; family history; biospecimens; and data on social, emotional, and cognitive development. This knowledge will be critical to help predict and prevent some of the known impacts of pre- and postnatal exposure to certain drugs or adverse environments, including risk and resilience for future substance use, mental disorders, and other behavioral and developmental problems.
In FY 2019, grants were awarded for Phase I of the study, which is an 18-month pilot phase during which awardees will test the experimental design and feasibility of methodological approaches. Awardees will conduct multisite pilot and feasibility studies around recruitment and retention, approaches to ethically structure the study and its data, and methodologies for brain imaging and other assessments, in order to provide the knowledge base to launch Phase II in FY 2021. Phase II will incorporate lessons learned from Phase I to create a fully integrated, collaborative infrastructure to support the collection and analysis of brain development and other data in opioid-exposed and non-drug-exposed infants and children across a variety of regions and demographics. NIH looks forward to continuing to support the study and reporting its progress and results.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $266.3 million, which is flat compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level. This includes $2.4 million for Research Management and Support related to this area of research.
Neuroscience and Behavior Research
NIDA’s Division of Neuroscience and Behavior (DNB) funds a research portfolio focused on advancing knowledge of the fundamental molecular, genetic/epigenetic, cellular, neurological, pharmacological, cognitive and behavioral processes that underlie SUD and its co-occurring conditions such as HIV. This includes identifying the effects of addictive substances on brain structure and function throughout the lifespan and across stages of drug use and SUD, from first exposure through abstinence, relapse, and recovery. Central to these goals are efforts to delineate the multiple biological (e.g., genes, epigenetic modifications, neural substrates, development) and environmental (e.g., stress, social, childhood adversity) factors that contribute to drug use, physical dependence, and SUD risk. Areas of emphasis include studies to identify genetic variants and epigenetic modifications that influence vulnerability to SUD, the effects of addictive substances on gene expression and brain development and function; the interaction of genes with environmental conditions, such as stress and early exposure to drugs that influence risk for SUD; and basic processes underlying resilience against SUD. DNB supports research to elucidate the pharmacology of drugs with respect to their molecular interactions with receptors, ion channels and other proteins and intracellular signaling pathways and to leverage this knowledge towards the development of therapeutics to treat SUD, the adverse consequences of addictive substances, and pain. The DNB portfolio also includes research on non-pharmacological SUD treatments including transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation, deep brain stimulation, and neurofeedback. DNB funds technology development that enables studies of the functional organization of the living brain—from cells to networks. This includes the interactions of complex neural circuits, the encoding of reward, craving, compulsive behavior, decision-making that may drive substance use, as well as the aversive responses to drugs that can inhibit drug-seeking. Advanced computational approaches, including theoretical modeling and novel methods for analyzing large, diverse data sets that enable the integration and simultaneous analysis of experimental data to better understand the neurobiological and behavioral consequences of drug use and SUD are supported by DNB. Finally, DNB supports mechanistic research towards addressing real-world challenges faced in clinical care of SUD, such as polysubstance use and comorbid psychiatric disorders. Spanning these areas of interest is research into how sex/gender and individual differences affect the SUD trajectory, including risk, resilience, and recovery and the basic neurobiology underlying SUD. Collectively, the research supported by DNB shapes perspectives on the effects of drugs on multiple biological systems and advances knowledge of the basic biological mechanisms that underlie drug use, thus guiding the development of novel prevention strategies and therapies for SUD.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $456.4 million, a decrease of $10.1 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
Epidemiology, Services, and Prevention Research
NIDA’s Division of Epidemiology, Services, and Prevention Research (DESPR or the Division) supports integrated approaches to understanding and addressing the interactions between individuals and environments that contribute to drug use, addiction, and related health problems. Through Monitoring the Future and other studies, DESPR is also monitoring trends in vaping and e-cigarette use, and the potential risks and health outcomes related to these behaviors. DESPR also supports research on integrating prevention and treatment services into healthcare and community systems to reduce the burden of drug problems across the lifespan. For example, ongoing research is exploring SUD treatment in the justice system, including studies on implementation of medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) and strategies for finding and screening people with SUD who are also at risk for HIV, as well as strategies for retaining them in treatment. NIDA also funds research into the efficacy of screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment in primary care settings for reducing drug use and SUD. Other program efforts focus on research to optimize implementation of evidence-based prevention interventions and treatment services in real-world settings. For instance, NIDA is funding researchers to partner with states as they use the State Targeted Response funding provided to SAMHSA in the 21st Century Cures Act to test approaches for expanding access to MOUD and naloxone for the reversal of overdose.
NIDA partnered with the Appalachian Regional Commission, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and SAMHSA to issue nine grants to help communities develop comprehensive approaches to prevent and treat consequences of opioid injection, including SUD, overdose, HIV, hepatitis B and C viral infections, as well as sexually transmitted infections. Funded in FY 2017, these projects work with state and local communities to develop best practice responses that can be implemented by public health systems in the nation’s rural regions.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $326.1 million, a decrease of $7.2 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
Therapeutics and Medical Consequences
NIDA’s Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences (DTMC) supports preclinical and clinical research focused on developing treatments for SUD. Since the pharmaceutical industry has traditionally made limited investments in this area, the responsibility for supporting the development of therapeutics has rested largely with NIDA. To most effectively leverage NIDA resources, DTMC encourages the formation of partnerships among pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic institutions, and other stakeholders with the common goal of expeditiously advancing new and repurposed compounds through the medications development pipeline toward FDA approval. For example, in collaboration with US WorldMeds, DTMC supported clinical trials on LUCEMYRA™, the first medication targeted specifically to treat the physical symptoms associated with opioid withdrawal.4 Having been shown to be safe and effective at managing withdrawal in patients discontinuing opioid use under medical supervision, LUCEMYRA™ was approved by the FDA in May 2018. NIDA also supports research to reduce the medical risks of compounds and to make them more feasible for pharmaceutical companies to complete costly phase IIb and III clinical studies for SUD indications.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $134.8 million, a decrease of $3.0 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
Clinical Trials Network (CTN)
The overarching mission of the NIDA Clinical Trials Network (CTN) is to allow medical and specialty treatment providers, treatment researchers, patients, and NIDA to cooperatively develop, validate, refine, and deliver new treatment options to patients. The CTN comprises: 18 research nodes with 34 principal investigators affiliated with academic medical centers and large health care networks; two research coordinating centers; and more than 240 community-anchored treatment programs and/or medical settings in over 40 States plus the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico. This unique partnership enables the CTN to conduct studies of behavioral, pharmacological, and integrated treatment interventions in rigorous, multisite clinical trials to determine effectiveness across a broad range of settings and patient populations. It also allows the CTN to ensure the transfer of research results to physicians, clinicians, providers, and patients. The network evaluates interventions, implementation strategies, and health system approaches to addressing SUD and related disorders, such as co-occurring mental health disorders and HIV.
The CTN is conducting studies to evaluate strategies for integrating OUD screening and treatment into emergency departments, pharmacies, primary care clinics, and American Indian/Alaska Native communities. It has also supported studies to capture important data for research on SUD in electronic health record (EHR) systems in primary care and emergency departments. The CTN is currently developing and testing a clinical decision support tool that integrates with EHR systems to help doctors diagnose OUD and either provide treatment or refer patients to appropriate treatment. Additional studies are investigating the effectiveness and safety of a combination pharmacotherapy for treatment of methamphetamine use disorder, assessing the effectiveness of OUD treatments for HIV-positive individuals with OUD, and improving the ability of healthcare providers to detect and address cocaine use using smartwatch technology. The CTN is also developing studies to examine the effects of medications for OUD in pregnant women and the effects of medical cannabis use using EHR data.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $40.1 million, a decrease of $0.9 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
High-Tech Biomedical Product Development
NIDA’s Office of Translational Initiatives and Program Innovations (OTIPI) takes research discoveries in prevention, detection, and treatment of SUD into candidate health applications for commercialization. Addiction (moderate to severe SUD) represents an underserved market, and OTIPI works to support early-stage commercialization of products in this area. OTIPI manages NIDA’s Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) Programs, utilizing novel fit-for-purpose funding authorities such as Prizes and Open Competitions, and establishing teaching programs that equip scientists with the competence to translate advances in addiction research into tangible solutions that our society needs.
Many of these efforts take the form of innovative new technology applications, from mobile apps that help patients find open beds in addiction treatment facilities or connect to support communities, to more sophisticated medical devices. Among OTIPI-funded technologies are: hospital bassinets delivering calming signals to infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome; alarms for detecting the early signs of a drug overdose; and virtual reality systems to manage pain and reduce opioid analgesic use.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $38.3 million, a decrease of $0.9 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
Intramural Research Program (IRP)
In addition to funding extramural scientists, NIDA conducts research in high priority areas through its Intramural Research Program (IRP). The IRP conducts multidisciplinary cutting-edge research to: 1) elucidate the mechanisms underlying the development of SUDs; 2) evaluate potential new therapies for SUDs, including pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions (e.g., psychosocial, neurofeedback, brain stimulation technologies, mobile health tools); and 3) identify and pharmacologically characterize emerging designer drugs such as synthetic opioids, stimulants, and cannabinoids, providing data-based evidence to the public on the dangers of these drugs.
One example of treatment evaluation at the IRP is a bench-to-bedside project in which IRP investigators are testing a novel compound to treat OUD. The compound activates the same receptors as traditional opioids but has only a subset of their cellular actions. IRP investigators are testing whether the compound reduces self-administration of opioids in a variety of animal models and, in parallel studies in people with OUD, whether it prevents opioid withdrawal with fewer side effects than treatment drugs in current use. If trials prove successful, this compound could be a new medication for OUD.
The IRP is also working with the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences on a dopamine D3 receptor antagonist that could be taken together with opioid pain relievers to reduce the chance of developing OUD. Preliminary animal studies have suggested that the compound reduces opioid self-administration and drug-seeking behavior without reducing the pain-relieving effects of opioids. This compound holds promise as an adjunct to opioid treatment for pain, and evidence suggests it could also be useful as a treatment for OUD.
Non-pharmacological addiction treatments are also being developed at NIDA. Research at the IRP’s on-site treatment-research clinic includes efforts to develop a smartphone app that detects or predicts stress, craving, and drug use via machine learning, on a time scale of hours—and a parallel project to develop the content that the app should deliver in a “just in time” fashion. Currently marketed apps purporting to serve these functions do not meet scientific standards of evidence for either their content or their risk-detection methods. The IRP is addressing that major gap in mobile health. Using passive measurement and digital phenotyping techniques, the IRP is also developing interventions and big data methodologies to prevent HIV transmission associated with high-risk sexual behavior in the context of substance use.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request is $98.0 million, a decrease of $2.2 million or 2.2 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level.
Research Management and Support (RMS)
Research Management and Support activities provide administrative, budgetary, logistical, and scientific support in the review, award, and monitoring of research grants, training awards, and research and development contracts. Additionally, the functions of RMS encompass strategic planning, coordination, and evaluation of NIDA’s programs, regulatory compliance, international coordination, and liaison with other Federal agencies, Congress, and the public. RMS staff at NIDA play leadership roles in helping to coordinate NIDA’s involvement in the NIH HEAL InitiativeSM, spearheading NIH’s response to the opioid overdose epidemic. In addition to the infrastructure required to support research and training, NIDA strives to provide evidence-based resources and educational materials about substance use and addiction, including information about timely public health topics such as opioid overdose prevention, marijuana research, use and consequences of vaping, synthetic drug trends, and medications for treatment of SUD including OUD.
The RMS portfolio also incorporates education and outreach activities to inform public health policy and practice by ensuring that NIDA is the primary trusted source for scientific information on drug use and addiction. Staff supported by NIDA’s RMS budget coordinate key activities that help to train the next generation of scientists and clinicians in the science of addiction and evidence-based approaches to treatment and prevention. In addition, NIDA’s RMS portfolio includes the NIDAMED initiative,5 which is aimed at engaging and educating clinicians in training and in practice in the latest science related to drug use and addiction.
Budget Policy: The FY 2021 President’s Budget request for RMS is $73.9 million, a decrease of $1.6 million or 2.1 percent compared with the FY 2020 Enacted level. Excluding HEAL funding for RMS, the request is $71.5 million, a 2.2 percent reduction from the FY 2020 Enacted level of $73.1 million.
References
- 2018 National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), SAMHSA, and www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html and /related-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates
- https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/index.html
- Nida supported science leads to first FDA approved medication for opioid withdrawal
- NIDAMED